Which of the Following Always Contains an Amino Functional Group
Answer 1 of 4. Which of the following statements about the monomers and.
An amino acid may be defined as an organic compound which contains amine -NH2 group a carboxylic -COOH group and alkyl -R group.
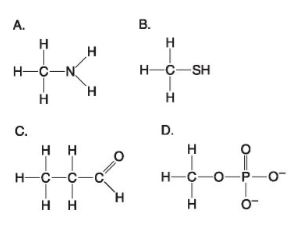
. Which of the following is an amino group a oh b nh 2. 1 Answer to Which of the following always contains an amino functional group. 11 Which of the following contains nitrogen in addition to carbon oxygen and hydrogen.
C It should dissolve in a nonpolar solvent. Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group. Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids.
Both groups are acidic. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Alcohol groups thiol groups carbon-carbon double bonds carbon-carbon triple bonds aromatic rings.
D amino and sulfhydryl. A ketone and methyl. The functional group of the amino acid.
23 Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids. Which of the following contains a carboxyl and amino group. Which of the following statements is true concerning this compound.
11 Which of the following statements about the functional groups of organic compounds is false. E hydroxyl and carboxyl 24 Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group. 13 Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group.
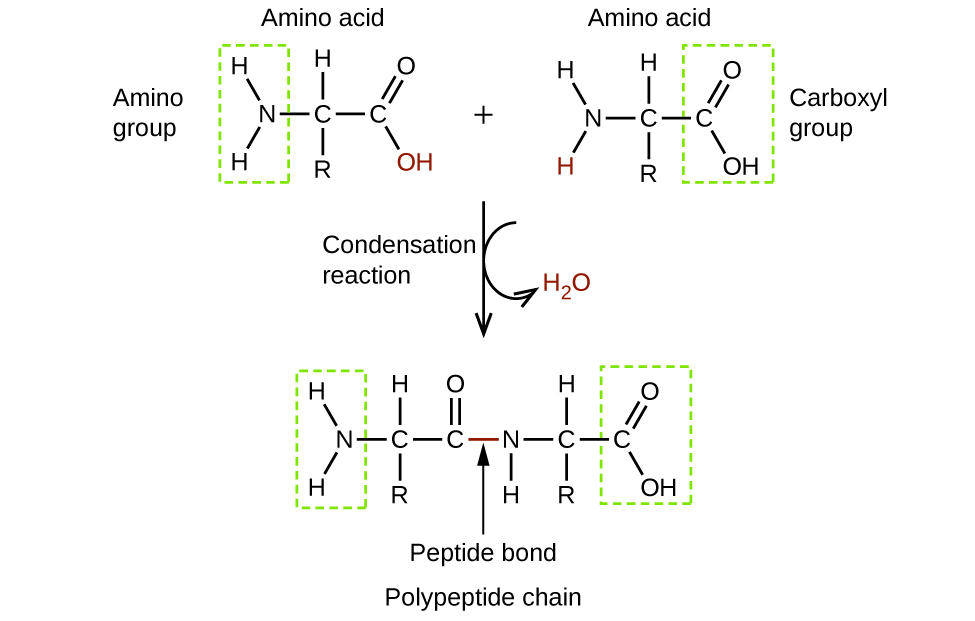
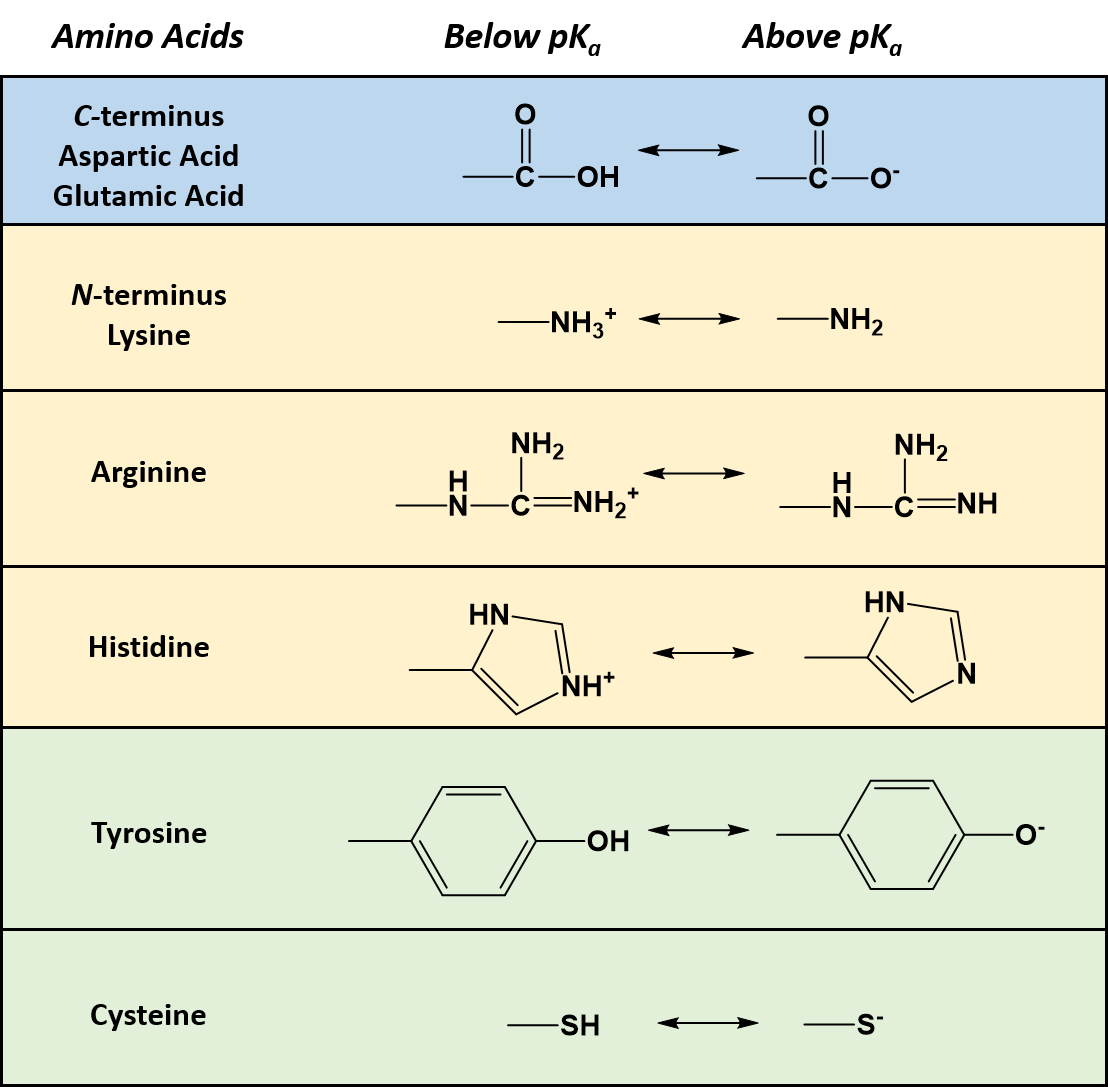
The general formula of amino acids is given as. These functional groups are in turn connected to a carbon atom and to the right and left of this carbon atom also identified as the backbone of the amino acid are the carboxylic acid COOH and amine group NH2. The two functional groups always found in amino acids are carboxyl and amino groups.
In addition proteins may contain a wide range of functional groups in the sidechains of the amino acid residues. Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group. CONH2 groups in asparagine and glutamine.
B carbonyl and amino. Be more constrained in structure. Like oxygen nitrogen is also more electronegative than both carbon and hydrogen which results in the amino group displaying some polar character.
This design and structure comprises what is called an amino acid. C carboxyl and amino. Organic molecules with only hydrogens and.
Alcoholic OH groups in serine and threonine. A carboxyl group consists of one carbon atom two oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom. Which molecule shown above contains a functional group that cells use to transfer energy between organic molecules.
A Functional groups help make organic compounds hydrophilic. Phenolic OH groups in tyrosine. A ketone and methyl B carbonyl and amino C carboxyl and amino D amino and sulfhydryl E hydroxyl and carboxyl D.
12 Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids. NH2 groups in lysine. 10 Which of the following is an amino group.
D It wont form hydrogen bonds with water. A molecule with the chemical formula C57H110O6 is an example of which type of organic molecule. Amino acids are comprised of a backbone that consists of a carboxylic acid COOH and an amine group NH2 linked by a carbon atom.
B - NH 2. Which of the following always contains an amino functional group. A compound contains hydroxyl groups as its predominant functional group.
All amino acids differ from one another in terms of -R group. The presence or absence of double bonds between the carbon atom and other atoms. Which of the following functional groups is found in all carbohydrates.
B It should dissolve in water. A It lacks an asymmetric carbon and it is probably a fat or lipid. Which of the following functional groups is capable of regulating gene expression.
The amino group consists of a nitrogen atom attached by single bonds to hydrogen atoms. An organic compound that contains an amino group is called an amine. A peptide bond occurs when the carboxyl group of one amino acid joins the amino end of another.
The linking carbon atom is also attached to a lone hydrogen H and the functional group of the amino acid. SH groups in cysteine. Which molecule shown above contains an amino functional group but is not an amino acid.
The following questions refer to the structures shown in Figure 45. COO groups in aspartic and glutamic acids. Therefore Amino and carboxyl groups are always found in amino acids.
E It is. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Carboxyl A hydrocarbon skeleton is covalently bonded to an amino group at one end and a.
Which of the following functional groups is abundant in fat. These amino acids will have their functional groups and their unique properties. Up to 256 cash back Which of the following always contains an amino functional group.
Compared to a hydrocarbon chain where all the carbon atoms are linked by single bonds a hydrocarbon chain with the same number of carbon aroms but with one or more double bonds will. A - OH B - NH C - COOH D - CO E - CH 2 3.
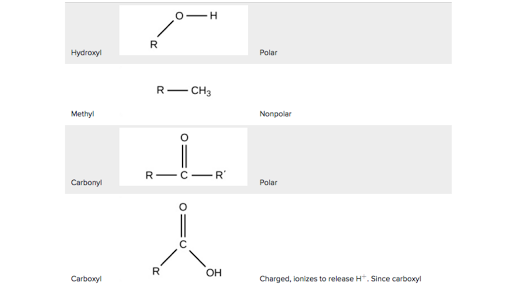
Functional Groups Carbon Biology Article Khan Academy

3 4 Functional Groups Biology Libretexts

What Are The Functional Groups In Amino Acids Quora

Rna Types 3 Main Types Of Rna With Diagram Diagram Type 3 Type

Biology Test Flashcards Quizlet

Biology Test Flashcards Quizlet
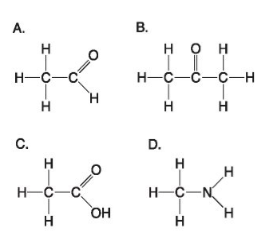
Chapter 4 Flashcards Easy Notecards
Amino Acids Introduction To Chemistry

Essential Amino Acids Chart Abbreviations And Structure Technology Networks

Chapter 4 Flashcards Easy Notecards
20 4 Amines And Amides Chemistry

Periodic Trends Ionization Energy Electron Affinity Chemistry

I Ve Always Used These In A Blender With Almond Milk Banana Pb2 And Some Ice The Girls And I Love It For Breakfa Plexus Products Plexus 96 Plexus Worldwide
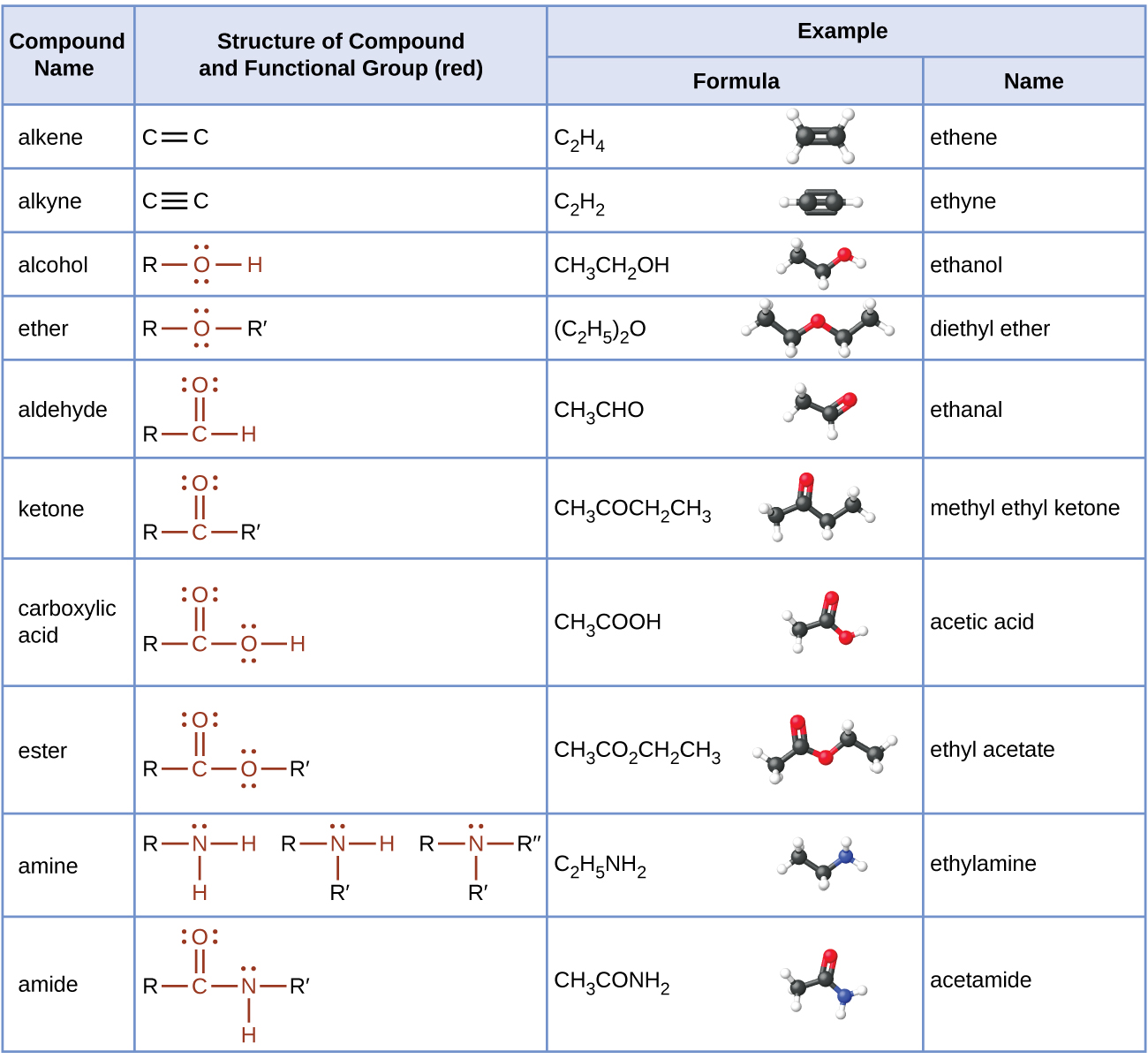
20 4 Amines And Amides Chemistry
3 4 Functional Groups Biology Libretexts

Which Two Functional Groups Are Always Found In Amino Acids



Comments
Post a Comment